The MINI is one of those special cars that gets to define the vehicle class it belongs to. What makes it even more individual is that it got to be awarded the “European Car of the Century” award. Let's have a closer look on how this car got to be what we know it is today.
the-history-of-mini
- Make: Array
- Model: the-history-of-mini
1959 - 2006 The History of Mini
- Make: Array
- Model: 1959 - 2006 The History of Mini
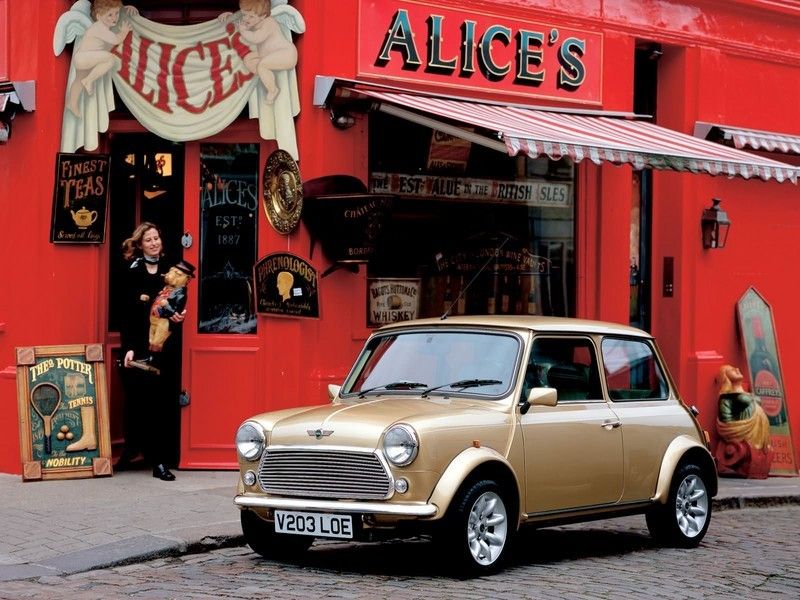
TheMini is the small car icon of the 1960s. It was produced by BMC (British Motor Corporation) starting with 1959 and was the first car to get the front-wheel-drive. This space saving solution influenced all the manufacturers, as nowadays FWD is the most popular drive-train layout. The new MINI was launched in 2001 and got to replace the legend with updates for the 21st Century.
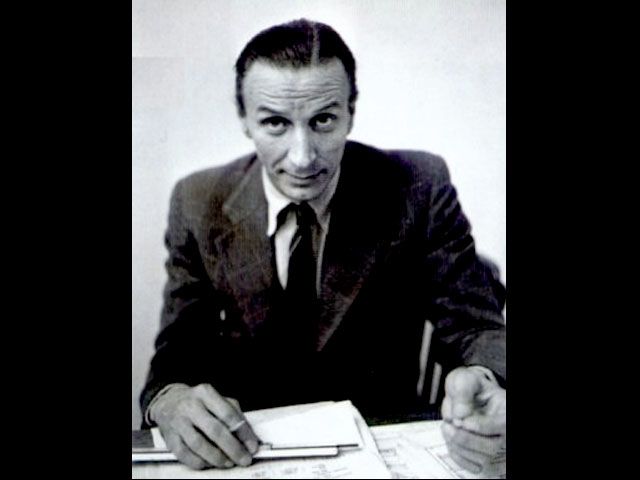
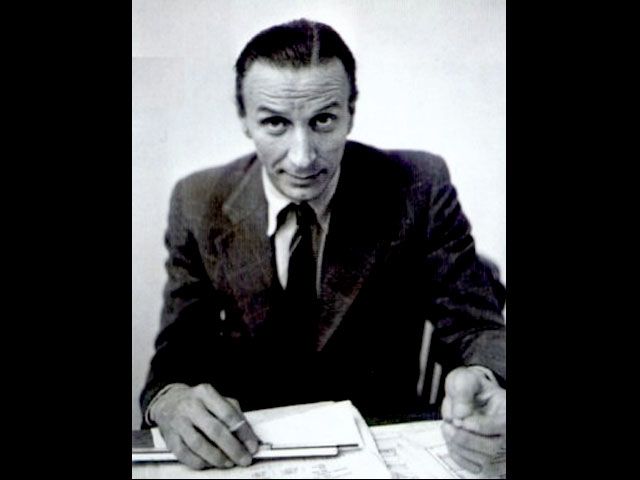
The revolutionary design of the Mini was created by Sir Alec Issigonis (1906–1988), considered a visionary in industrial transportation. It was intended as an affordable vehicle in response to the oil crisis. Along its production period it was built at the Cowley plants in the United Kingdom, and afterwards in Australia, Belgium, Chile, Italy, Portugal, South Africa, Spain, Uruguay and Venezuela.
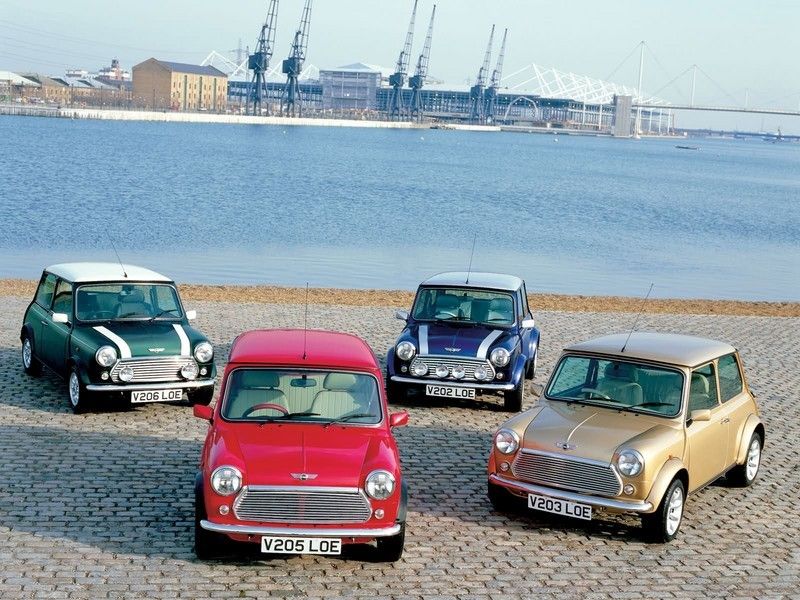
The first Mini, called the Mk I had three important updates: The Mk II, the Clubman, and the Mk III. Sportier versions were the Mini Cooper and the Cooper"S", that got to successful as rally cars. They even get to win the Monte Carlo Rally three times.
Design and development
The Mini was designed as a result of the 1956 Suez Crisis, which reduced oil supplies, and forced the UK government saw to introduce petrol rationing. Obviously, the sales of large cars, with high fuel consumption dropped and the market for so called “bubble cars” boomed. BMC realized that they had to produce a small vehicle fast.
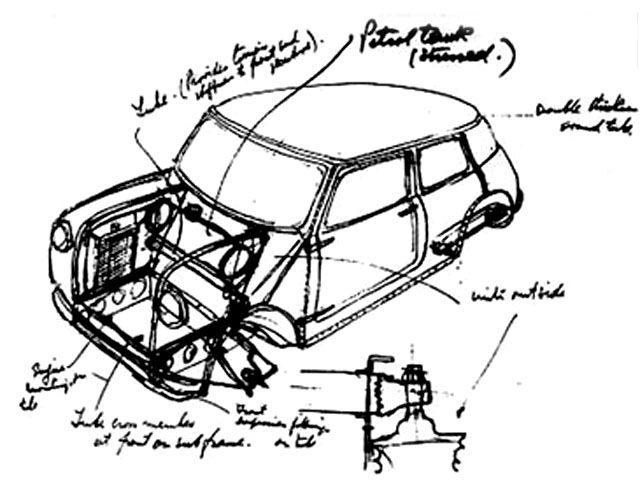
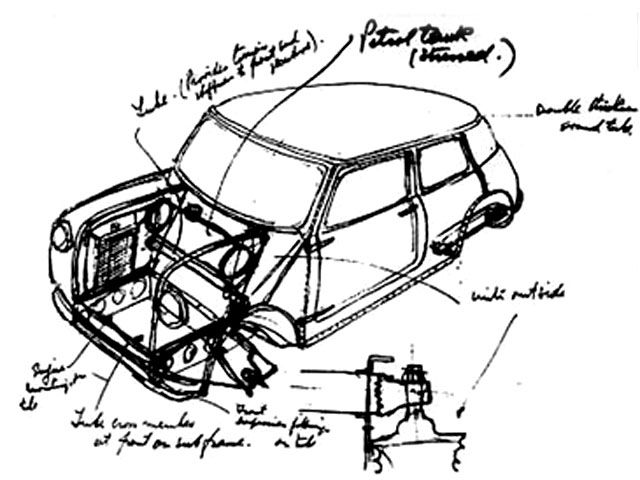
Issigonis, that was reputed as being very skilled in designing small vehicles was assigned to this task. Together with a small team of designers Issigonis got to produce the original prototype by October 1957. The new vehicle was using a conventional BMC four-cylinder water-cooled engine, but had the innovation of mounting it transversely with the the engine oil lubricated, four-speed transmission placed in the sump, and with FWD.
All of the small FWD cars developed since the 70s have used a similar configuration. Another innovation was the placement of the radiator at the left side of the car so that the engine-mounted fan could be retained, but with reversed pitch so it blew air into the natural low pressure area under the front wing. This saved a lot of vehicle length, but had the short coming of feeding the radiator with air that had been heated by passing over the engine.
Also the slinding windows in the doors allowed for storage pockets to be fitted in the space where a winding window mechanism would have been. A gossip says that Issigonis sized the resulting storage pocket to fit a bottle of his favorite gin. Another smart feature was the boot lid that had the hinges at the bottom, so that the car could be driven with it open to increase luggage space. The MK I models had a hinged number plate that dropped down to remain visible when the boot lid was open.
Another goal of the designers of that of keeping the manual labour costs as low as possible. The simple construction of the car included quirky welded seams that were visible on the outside of the car and also external door and boot hinges.
All of these smart technical novelties produced a car with minimum overall dimensions and maximized space for passengers and luggage.
Other enhancements included the mounting of the carburetor at the back of the engine. This allowed for an extra reduction gear to be mounted between the engine and the transmission to reduce loads on the gearbox and prevent rapid wear. The engine had 51.7 cui and offered an excellent a top speed for this type of a car of 72 mph.
Although the Mini’s design had utilitarian origins the shape of the classic model had become so iconic that by the Rover Group, the heirs to BMC, have registered it as a trademark in the early 90s.
History
The Mk I
The First Mini in production version shown to the press in April 1959, and by August several thousand vehicles had been produced ready for sales.
The name “Mini” was not used form the beginning of production. In early advertising material was used the name “SE7EN”. An already famous Morris model at that time was the Minor, which is Latin for “smaller”. So, for the even smaller car the decided to use the abbreviation for the Latin word “minimus”, which means “the smallest”.
In 1964 the MK I got a new suspension design using the “hydrolastic” system. This created a softer ride but was criticized by many for being too expensive and altering the handling of the car. Starting with 1971 the original rubber suspension was back again, and used until production end.
The sales were not very promising after the launch, but the Mini became a hit through the 60s, with a total of 1,190,000 Mk I's produced. It is being rumored that the MK I wasn’t profitable for BMC, because it was sold at a lower price than the production costs, in order to be competitive on the market. Some even say that was due to an accounting error. A thing is for sure though, that the MK I got its own place into the culture of the 1960s.

The Mk II
In the late 60s Issigonis had been working for a replacement for the original Mini. That was supposed to be shorter and more powerful than the MK I, but due to management decisions at BMC it was not built. Instead of that the Mk II was released, featuring a redesigned front grille (which remained like that from that point) and also a larger rear window among other cosmetic changes. The Mk II Minis was produced in 429,000 pieces.
The Mk III
The Mk III Mini had a series of body modifications, the most serious of which were the larger doors with concealed hinges. Also the suspension was reverted from Hydrolastic to rubber system for cost-saving purposes. Also the boot lid lost the original hinged number plate got instead a large rear colour coded lamp. It also featured larger rear side windows.
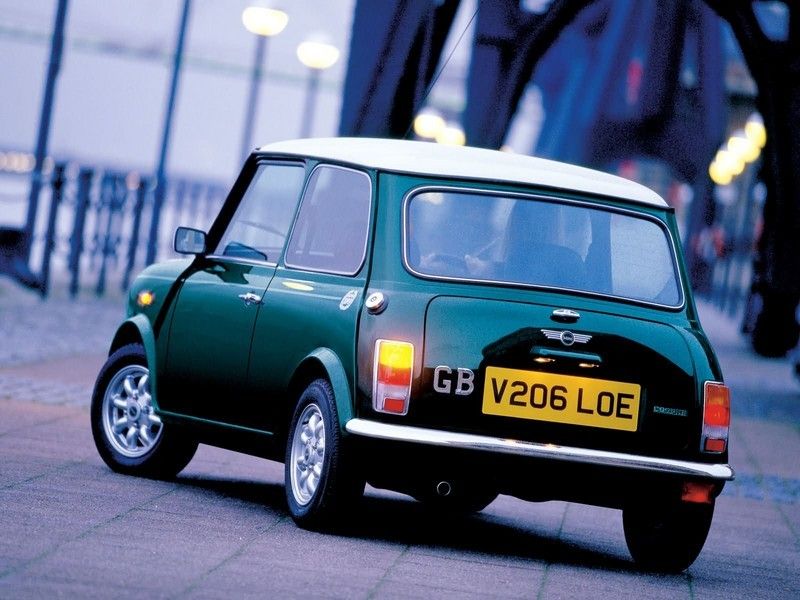

The Mk IV-VII
The later MKs, IV to VII featured mainly technical modifications that included a front rubber mounted sub-frame with single tower bolts, twin stalk indicators with larger foot pedals, 8.4 inch brake discs and plastic wheel arches. Beginning with 1990 engine mounting points were moved forward to accommodate 78 cui power units with the HIF carb version.
Through the 1980s and the 1990s there were released several "special editions" of the Mini, that shifted the car from a mass-market item into a fashionable icon. Maybe for this reason the Mini become such an asset for BMW, which in 1994 bought the brand as part of the Rover Group.
Under BMW supervision the Mini received an airbag to comply with European safety legislation. Because by the year 2000 Rover Group was still suffering massive losses, BMW decided to sell MG, Rover and Land Rover and only kept the Mini brand in order to produce a new model with that name
The final Mini MK VII was produced in October 2000, being the last from a total of 5.3 million cars manufactured and sold all over the world.
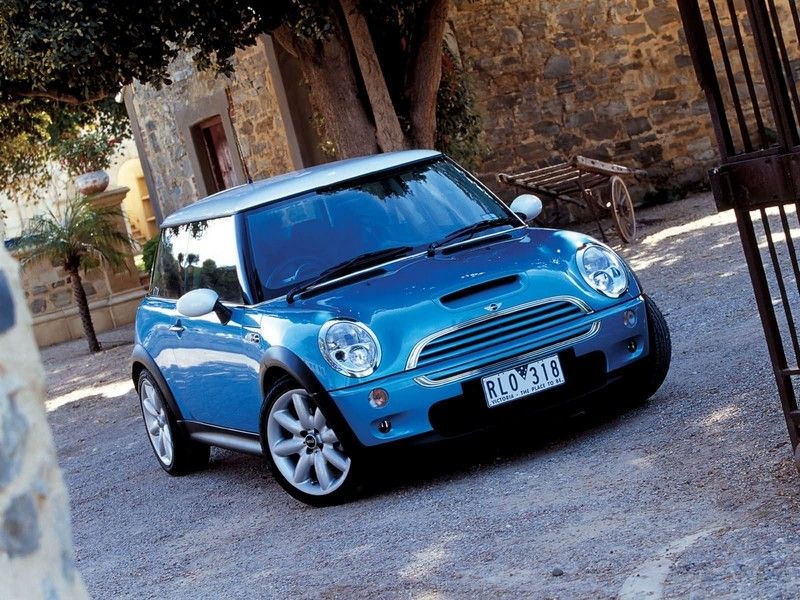
The new BMW MINI
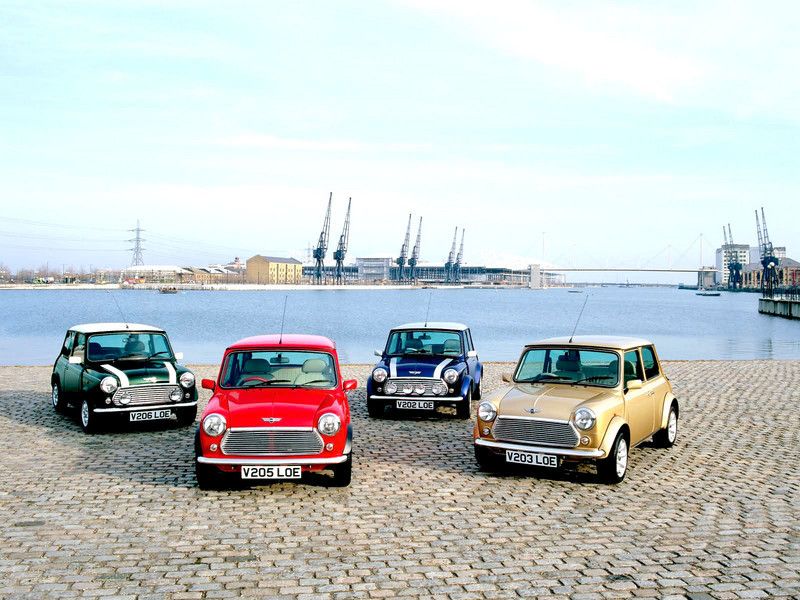
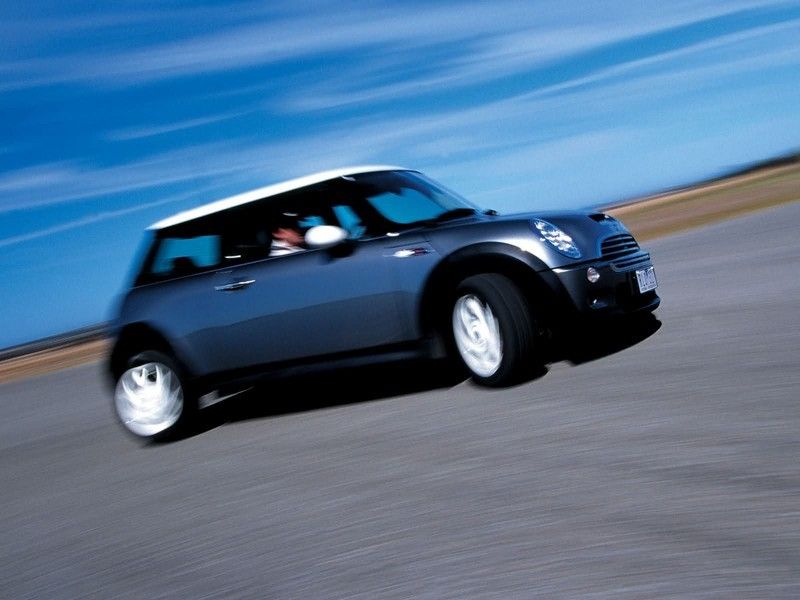
After production of the classic Mini ended in 2000, BMW, the new owner, announced a successor to the Mini – which was called the MINI (written in capital letters).
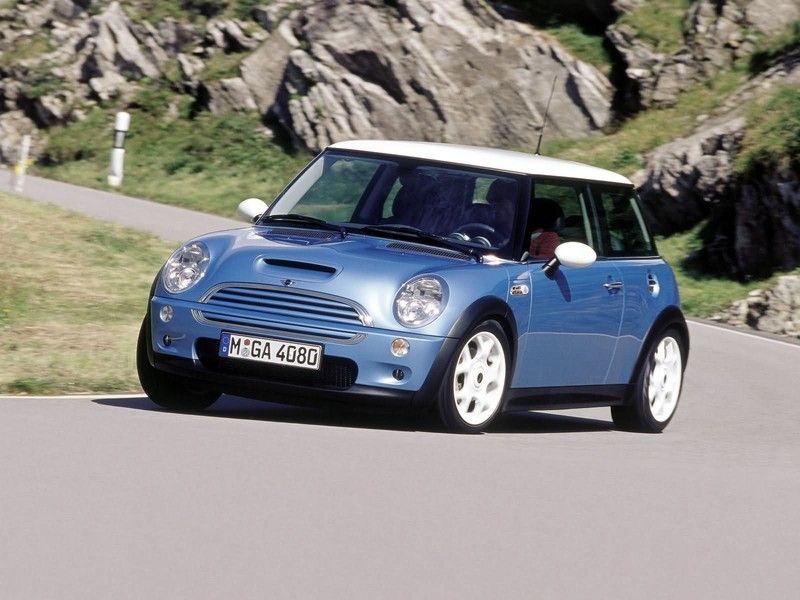
The MINI shares the FWD architecture of its predecessor, but is no longer an affordable vehicle. It seems to have also inherited the sporty and luxurious genes of the BMW premium brand. With top technology for this vehicle class, the MINI is now an object of fashion, oriented towards the pleasure of driving. In comparison with classic, the new car is around 21 in longer, 12 in wider and weighing 2300 lbs, rather than 1450 lbs. All of that and the departure from the minimalism of the classis become objectionable for some Mini fans. Market success proves that the new car is fitted for the 21st Century when comfort, safety and environment requests are harsher.
For comparison we are offering you the technical details for the 1964 Austin Mini Cooper S and the 2006 BMW MINI Cooper S
 -----
-----
1964 Austin Mini Cooper S Specs
2006 BMW MINI Cooper S Specs
engine Supercharged Inline-4
gear ratios 4.167:1, 2.620:1, 1.970:1, 1.605:1, 1.335:1, 1.083:1
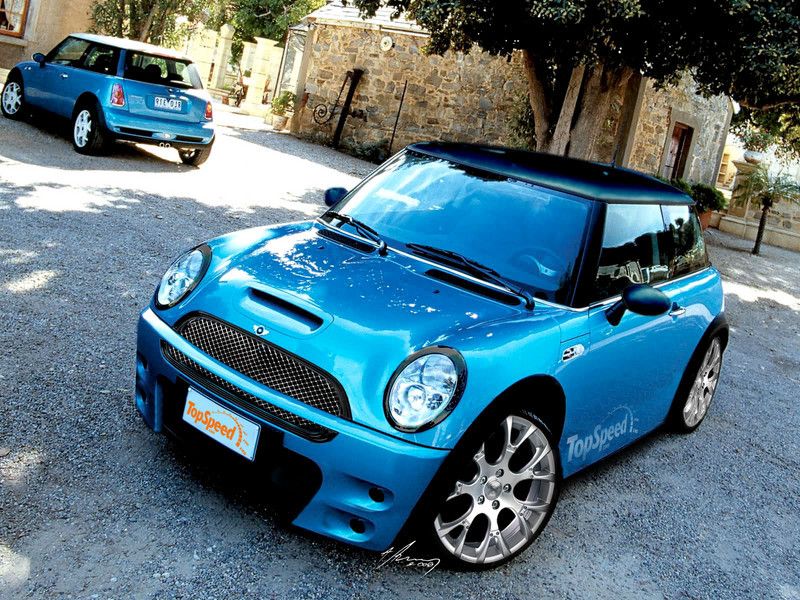
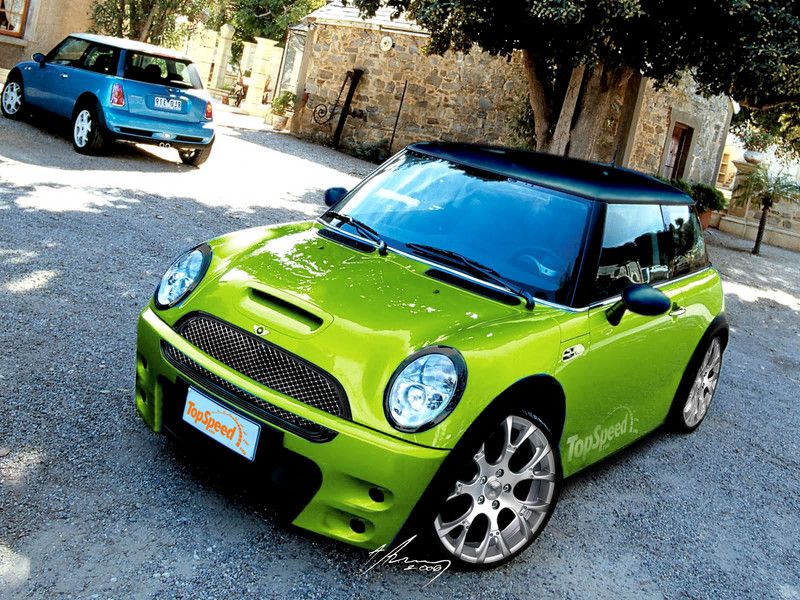
TopSpeed artists tuning recommendation
Ourartists have worked out a tuning proposal for your new MINI Cooper S. An aggressive front spoiler should meet the lower ride-height and reduce lift. It would feature on each side dual brake-feed air intakes and a central radiator-cooling grid. Also, we would like to remove the original chrome details of the front and replace them with some with a darker tint. The original front grid can be successfully replaced by a metallic net, like those found on Bentley or Jaguar. Lower side-skirts further tune aerodynamics. We would like to see on this car “Tecnomagnesio Sao Paulo” 12*19 inch wheels. Don’t forget a “TopSpeed” sticker on each side for credits and coolness. Should be served hot as it is!