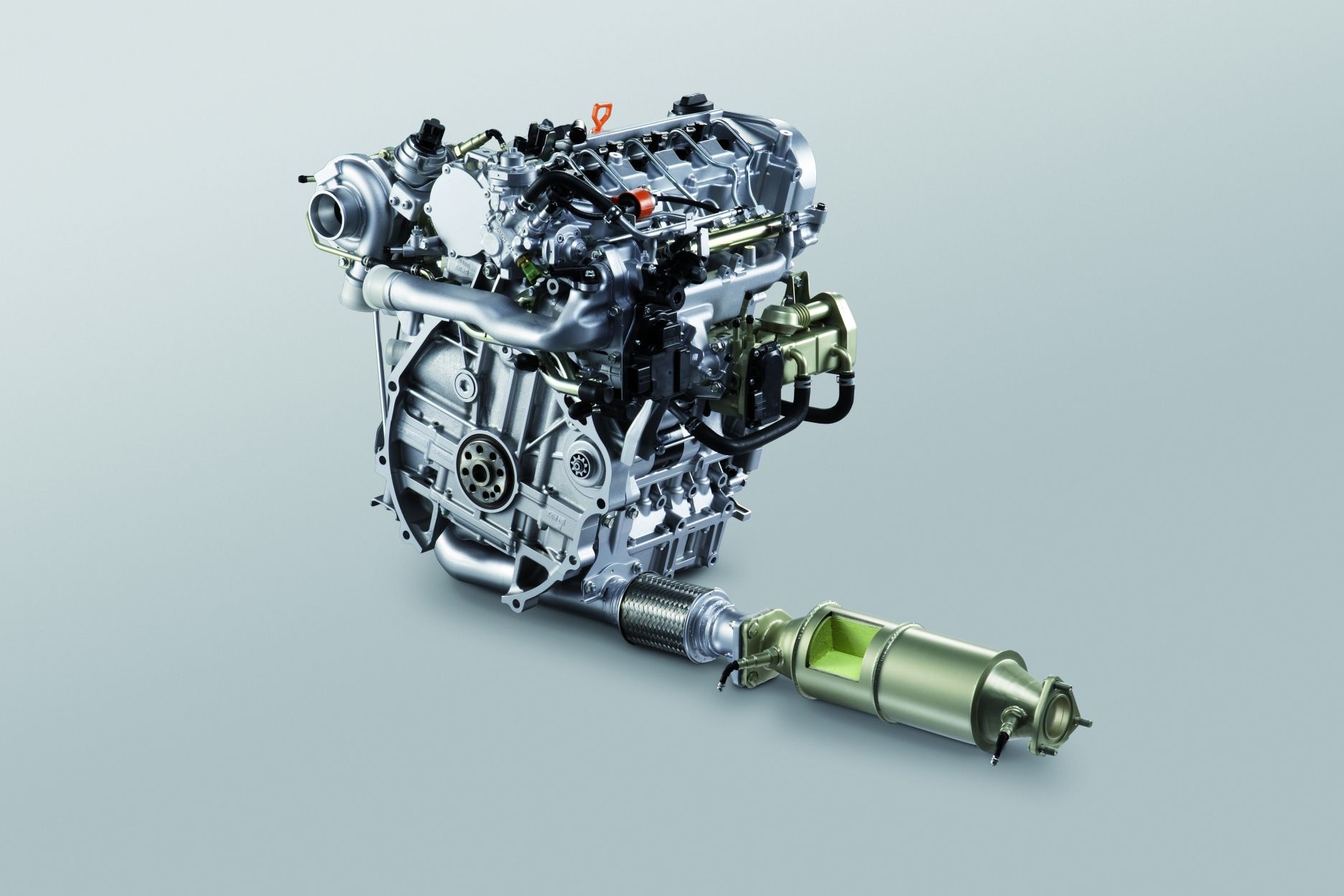
Honda's next-generation diesel engine uses advanced technology to reduce NOx emissions – making it one of the world's cleanest diesel units.
Its revolutionary catalytic converter reduces emissions of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) to match those of a petrol engine. This low level is sufficient to meet the stringent US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Tier II/Bin 5 emissions requirements.
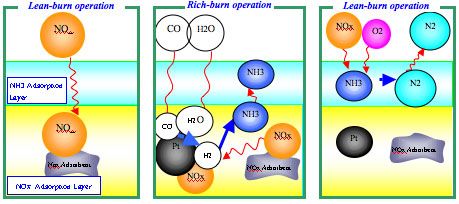
The catalytic converter uses an innovative system that uses the reductive reaction of ammonia to ‘detoxify’ NOx by turning them into harmless nitrogen. However, unlike Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems that use urea injection supplied from a storage tank, Honda’s latest technology uses ammonia generated directly within the catalytic converter.
It features a two-layer structure: one layer adsorbs NOx from the exhaust gas which, during periodic rich burn controlled by the engine management system, reacts with hydrogen obtained from the exhaust gas to produce ammonia; the latter is then adsorbed by the second layer. During lean burn operation, the ammonia is used to convert the remaining NOx in the exhaust, since ammonia is a highly effective reagent for reducing NOx into nitrogen in oxygen-rich, lean-burn atmospheres. The system also provides enhanced NOx reduction efficiency in the most critical temperature range of 200-300°C for diesel engine exhaust gas systems.
Petrol engines presently employ three-way catalytic converters that offer NOx reduction rates as high as99 per cent, but this performance is possible only at the stoichiometric air fuel ratio.
In the oxygen-rich environment of a lean-burn diesel engine, three-way catalytic converters only reduce NOx levels by approximately 10 per cent. Honda’s new technology efficiently reduces NOx in a lean-burn atmosphere, enabling diesel engines to rival gasoline engines in cleanliness. The compact system is also easy to install in passenger vehicles. Installation is downstream of the standard diesel oxidation catalytic converter and diesel particulate filter (DPF).
Alongside its development of exhaust gas cleaning technology, Honda also plans to address other technical challenges in developing clean diesel engines, such as handling diesel fuels with different cetane numbers (a problem in some markets) and meeting US On-Board Diagnostic System requirements.
Honda plans to introduce its next-generation diesel engine within the next three years.